Did you know there are 13 types of vitamins your body needs? Most of these vitamins are either not produced by the body or available in insufficient amounts.
Therefore, it becomes necessary to supplement the low vitamin levels through diet or supplements. Vitamins can either be water soluble or fat soluble.
One of the essential Vitamins in the body is Vitamin D, popularly known as the “sunshine vitamin.” It’s a fat-soluble vitamin.
Every cell in the body has a receptor for the vitamin, which causes the skin to produce cholesterol when exposed to sunlight.
Vitamin D is also available in certain foods such as grains, fortified foods (margarine), fatty fish (tuna), dairy products (milk), mushrooms, and egg yolks.
Vitamin D occurs in two variants of Vitamin D2 and D3. The two vitamins differ structurally.
However, according to NCBI, the active form of the vitamin is the same in both variants.
The active form of vitamin D is called Calcitriol. Even though vitamin D seems like an easy-to-acquire vitamin, especially since most people are exposed to the sun, research conducted by Harvard University has shown that over a billion people worldwide suffer from Vitamin D deficiency.
This is worrying since deficiency of the vitamin in the body causes illnesses and other health conditions that can lead to dire consequences if not watched.
What Happens When You Have Low Vitamin D?
Rickets
Rickets is the best-known disease caused by a lack of vitamin D in children. It causes soft and weak bones, especially in the lower limbs, hence vulnerability to skeletal deformities.
Right from birth, a child’s vitamin D levels should be kept in check to ensure they don’t develop rickets.
Liquid vitamin d for newborns can be administered to protect them from rickets and other effects of vitamin D deficiency.
Children should also be fed with foods rich in vitamins and allowed enough sunbathing time.
Weak, Thin, or Brittle Bones
Vitamin D is essential for the absorption of calcium in the body so you can have strong bones. With the required levels of the vitamin, the body can mineralize bones to keep them healthy.
However, if the level of vitamin D is low, there is low absorption of calcium.
It’s then released from your bones to compensate for the deficiency in the blood, leading to weak, thin, and brittle bones, a precursor for Osteoporosis.
Fractures
Many studies have been conducted to assess the relationship between the deficiency of Vitamin D and fractures. One such study was performed on men and women aged 65 and older. It indicated a 33% lower rate of fractures in persons who took Vitamin D supplements.
Weak Muscles
Research has shown that there is a correlation between cellular growth in muscle cells, increased protein synthesis, and improved musculoskeletal body functions in people with the correct levels of Vitamin D. All these are associated with strong muscles.
On the contrary, it has been shown that people deficient in Vitamin D are likely to have impaired muscle functions even before they present symptoms of bone problems. For instance, the early signs of vitamin D deficiency are indicated when individuals fall easily.
Inflammation
Research conducted on adults with high blood pressure treatment.
It shows that those with high levels of Vitamin D in their bodies suffer less inflammation than those with less.
It also is shown in a different study that involved people suffering from osteoporosis.
The study results indicated that respondents who took Vitamin D supplements suffered less inflammation than those that didn’t.
Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia is a condition that arises from softening of the bones in adults with a high deficiency of Vitamin D.
According to the Mayo Clinic, people suffering from this disease are likely to break bones, especially in the ribs, legs, and spine. Treatment is usually by eating a diet rich in Vitamins especially Vitamin D and getting enough sunbathing time.
Infections
People who are deficient in Vitamin D are predisposed to getting infections such as the common cold and respiratory tract infections.
Recent studies have also been carried out to show the correlation between Vitamin D levels and other infections such as Pneumonia and UTIs.
How do you know when you are short of vitamin D in your body?
Here are some signs and symptoms that should indicate when you need to get checked or supplement your intake of Vitamin D:
Signs and Symptoms
Depression
Lack of sunlight is associated with depression for many years. In recent studies, it has been shown that low levels of Vitamin D in the body lead to depression, especially in old age.
The relationship between vitamin D and depression is related to the fact that the vitamin facilitates the secretion and production of hormones such as adrenaline, dopamine, noradrenaline, and serotonin.
Therefore, if the levels of these hormones are disrupted, depression is likely to occur.
Severe Hair Loss
People who don’t get enough vitamin D are likely to experience severe hair loss, especially women. Although there isn’t enough research on this, it has been shown that most people suffering from hair loss have low levels of Vitamin D.
Muscle Pain
Muscle pain is another symptom that indicates a low Vitamin D levels. In a study done to investigate the relationship between “Vitamin D and central hypersensitivity in patients with chronic pain,” it was found that 71% of the patients with chronic pain had a deficiency of the vitamin.
Bone Loss
Vitamin D also helps in the absorption of calcium in the body.
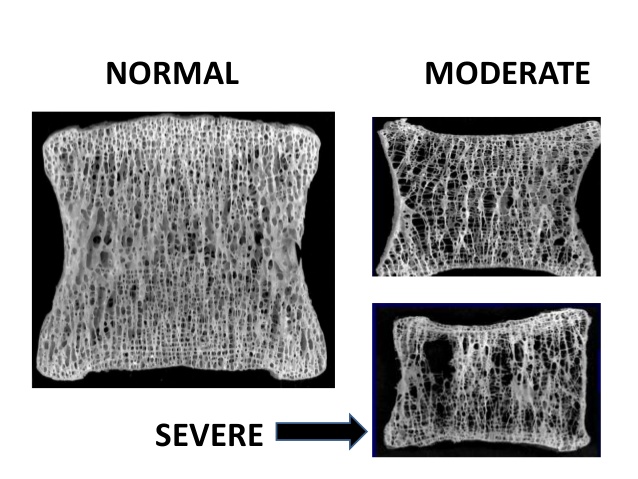
Some patients, according to Healthline, suffer from bone loss as a result of vitamin D deficiency, but not a lack of calcium.
Bone pain, back pain, increased risk to die from cardiovascular diseases, fatigue, impaired wound healing, severe asthma in children, tooth decay and cognitive impairment are other signs and symptoms of vitamin D deficiency.
Treatment and Causes
Treatment of Vitamin D deficiency is done through medication, given in the form of supplements and diets. The required amounts of Vitamin D vary depending on your general health, age, sex, and exposure to sunlight.
Causes of Vitamin D deficiency include lack of a vitamin D-rich diet.
Limited exposure to sunlight, dark skin with high concentrations of melanin which inhibits the absorption of the sun rays, the inability of the kidneys to convert the vitamin to Calcitriol (the active form), weight gain or obesity, and failure of your body to absorb Vitamin D adequately into the system.
The vitamin D levels in the body should be kept between 20 ng/mL and 50 ng/mL. There are also side effects that result from consuming excess vitamin D.
Therefore, a blood test is essential to determine how much Vitamin D you have in your body.
According to the Institute of Medicine, IOM, the RDA for Vitamin D is 600 international units for children and adults at the age of 70, and 800 IU for people aged over 70.
Contact us today to find out more about vitamin D deficiency and how you can counteract its side effects